Inventory : Any business process that involves goods going in or coming out of a firm’s inventory. It generally includes receiving, temporary storage, labeling and storage, withdrawal, issue, and movement of the item through work-in-process routine.
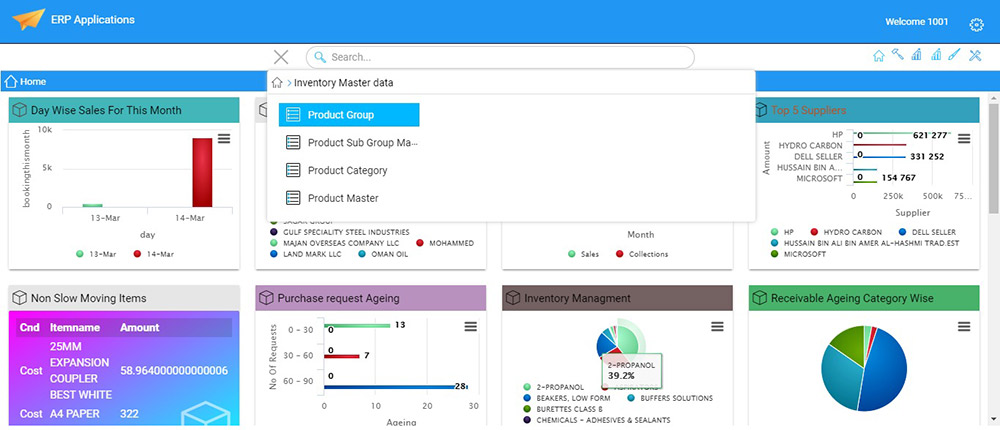
Masters : Master data information will be stored in Product group , product sub group, product categories and product master.
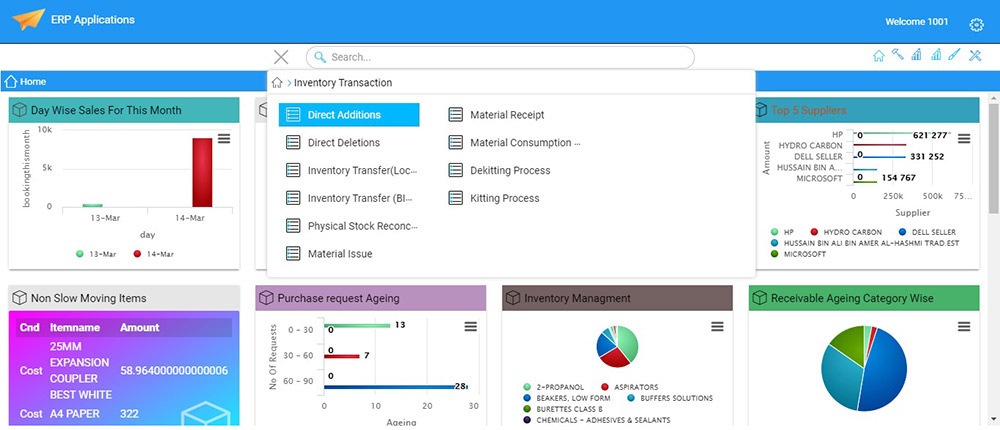
Transactions :
Inventory Issues
Issuing inventory typically involves removing items from a branch/plant or location, adjusting the inventory balance, and recording the transaction in the GL. You can also remove only the cost amounts for an inventory record to devalue the items.
Tasks that relate to issuing inventory items include:
- Recording the use of inventory items by an operating department in the company.
- Removing obsolete or damaged goods.
- Issuing inventory to a job.
- Charging inventory that is used for the repair or maintenance of equipment.
Inventory Receipt
When a company receives a shipment of inventory, it might not include an invoice but rather a bill of lading which details the items shipped and the cost
Inventory Transfer
You can use transfer transactions to record two types of inventory movement:
- Movement between different locations in the same branch/plant.
- Movement between different branch/plants.
Direct addition
You can enter adjustments to increase the on-hand quantity and the cost of inventory items in a branch/plant without conducting a complete physical inventory. For example, you can adjust inventory when a discrepancy exists between the number of items that are recorded for a location and the actual count.
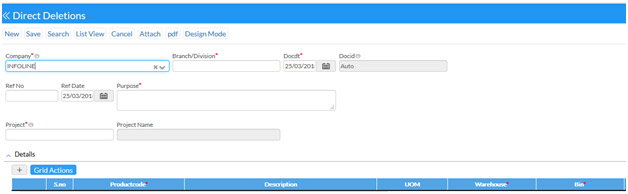
Direct Deletion
You can enter adjustments to decrease the on-hand quantity and the cost of inventory items in a branch/plant without conducting a complete physical inventory. For example, you can adjust inventory when a discrepancy exists between the number of items that are recorded for a location and the actual count.
Physical stock Reconciliation
Stock Reconciliation is the process of counting and evaluating stock-in-trade, usually at an organisations year end in order to value the total stock for preparation of the accounts. In this process, actual physical stocks are checked and recorded in the system.