The specific planning of the usage and management of a company’s financial resources to attain its objectives as a business concern and return maximum value to shareholders.
Strategic financial management involves precisely defining a company’s business objectives, identifying and quantifying its resources, devising a plan for utilizing finances and other resources to achieve its goals, and establishing procedures for collecting and analyzing data, making financial decisions, and tracking and analyzing variance between budgeted and actual results to identify problems and take appropriate corrective actions.
Accounts Payable -AP
An accounting entry that represents an entity’s obligation to pay off a short-term debt to its creditors. On many balance sheets, the accounts payable entry appears under the heading current liabilities. Another common usage of AP refers to a business department or division that is responsible for making payments owed by the company to suppliers and other creditors.
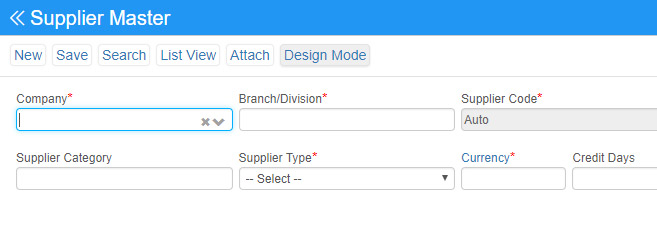
Supplier Master: Central data pool in which all your supplier information master data are stored and managed.
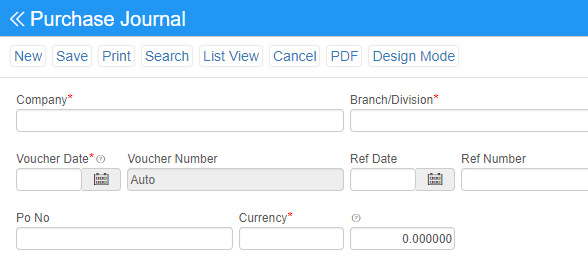
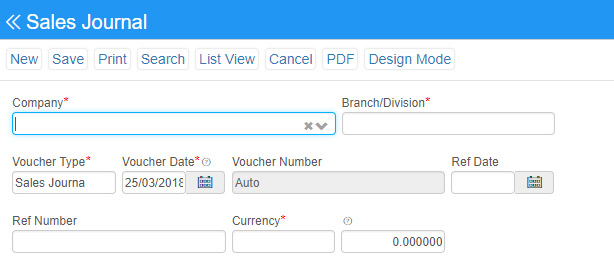
Purchase journal: A purchases journal is a specialized type of accounting log that keeps track of orders made by a business on credit or on account. Cash purchases for inventory are not tracked in the purchases journal. The amount of detail provided in a purchases journals determined by the type of purchase and products received.
PDC Payment: A postdated check is a check on which the issuer has stated a date later than the current date.
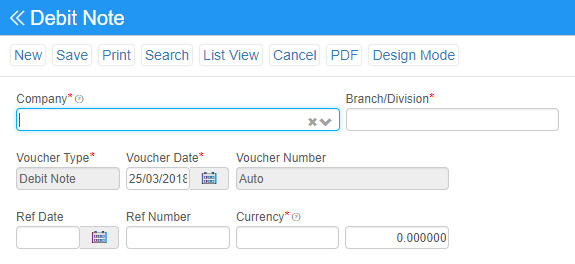
Debit Note: A debit note or debit memorandum (memo) is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller as a means of formally requesting a credit note. Debit note acts as the Source document to the Purchase returns journal. In other words, it is an evidence for the occurrence of a reduction in expenses.
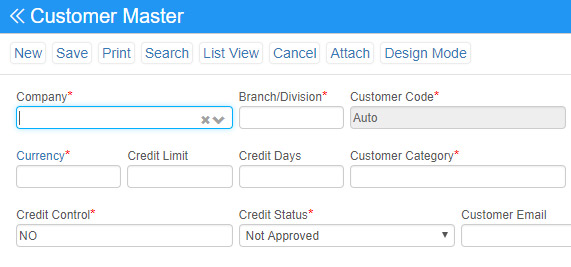
Accounts Receivable – AR: Accounts receivable refers to the outstanding invoices a company has or the money the company is owed from its clients. The phrase refers to accounts a business has a right to receive because it has delivered a product or service. Receivables essentially represent a line of credit extended by a company and due within a relatively short time period, ranging from a few days to a year.
Sales journal: A sales journal is a specialized accounting journal and it is also a prime entry book used in an accounting system to keep track of the sales of items that customers(debtors) have purchased on account by charging a receivable on the debit side of an accounts receivable account and crediting revenue on the credit side.
PDC Receipt: A postdated check is a check on which the issuer has stated a date later than the current date
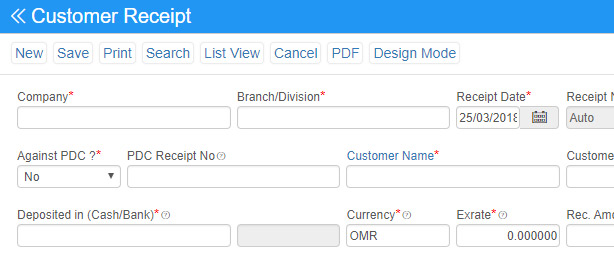
Customer Receipt: When the customer pays their invoices you can record this from the Customer Receipt option. The receipt will be either cash or Bank.
Credit Note: A credit note or credit memorandum (memo) is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer. Credit notes act as a Source document for the Sales return journal. In other words the credit note is evidence of the reduction in sales.